Carbon Sequestration Process Reading Answers
Carbon Sequestration Process Reading Answers is an academic reading answers topic. Carbon Sequestration Process Reading Answers has a total of 7 IELTS questions in total. Choose the Correct letters A-D, And Do the following statements agree with the information given in the text above? Write yes, no, and not given.
The candidate's understanding and assessment of academic and general texts are examined in the IELTS Reading Section. Using IELTS Reading Practice Questions, you can increase your vocabulary, sharpen your critical reading skills, and become more familiar with the various question types in reading tasks. Furthermore, practice enhances vocabulary and improves analytical reading skills, both of which are necessary for success. It's crucial to understand the guidelines for each question type and develop effective strategies to manage time and achieve excellent band scores.
Check: Get 10 Free Sample Papers
Check: Register for IELTS Coaching - Join for Free Trial Class Now
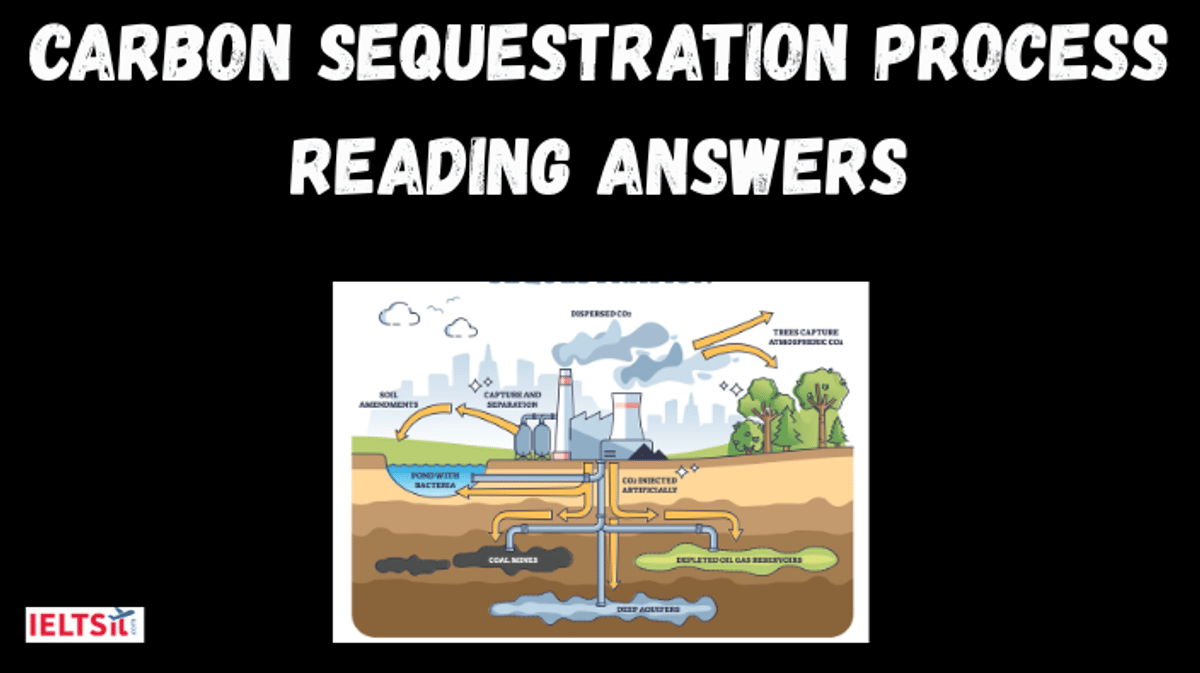
Topic:
CARBON SEQUESTRATION PROCESS
Carbon sequestration is the process involved in carbon capture and the long-term storage of
atmospheric carbon dioxide or other forms of carbon to mitigate or defer global warming. Carbon dioxide (C02) is naturally captured from the atmosphere through biological, chemical, and physical processes. Artificial processes have been devised to produce similar effects, including large-scale artificial capture and sequestration of industrially produced CO2 using subsurface saline aquifers, reservoirs, ocean water, aging oil fields, or other carbon sinks.
Carbon sequestration may refer specifically to:
- The process of removing carbon from the atmosphere and depositing it in a reservoir. When carried out deliberately, this may also be referred to as carbon dioxide removal, which is a form of geoengineering.
- Carbon capture and storage, where carbon dioxide is removed from flue gases (e.g., at power stations) before being stored in underground reservoirs.
- Natural biogeochemical cycling of carbon between the atmosphere and reservoirs, such as by chemical weathering of rocks.
There are three ways that this sequestration can be carried out: post-combustion capture, pre-combustion capture, and OXY-combustion. A wide variety of separation techniques are being pursued, including gas phase separation, absorption into a liquid, and adsorption on a solid, as well as hybrid processes, such as adsorption/membrane systems. The above processes basically will capture carbon emitted from power plants, factories, fuel-burning industries, and so on.
Biological Sequestration is typically accomplished through conservation practices that enhance the storage of carbon (such as restoring forests, wetlands, and grasslands) or reduce CO2
emissions (such as reducing agricultural tillage and suppressing wildfires). Soil carbon sequestration is the process of removing CO2 from the atmosphere by plants accumulating organic matter in soil. For example, when plant materials and roots are decomposed by microbial action (microbes and macro fauna, such as worms), stable forms of carbon in soil are created. In agriculture, soil carbon sequestration can be achieved by land management practices, such as planting cover crops and incorporating crop residues into the soil. However, the amount of carbon sequestered at a site depends on a balance between incorporation and release mechanisms. Land use, disease, tillage, erosion, and disturbances magnified by climate pressures such as wildfires and droughts can release biologically sequestered CO2 back into the atmosphere. Therefore, efforts to increase biological sequestration are focused on increasing carbon storage while simultaneously avoiding disturbances that cause C02 emissions.
Questions 15-17
Choose the Correct letters A-D
15. Which of the following options is not a method used for carbon sequestration?
A. air-combustion
B. post-combustion capture
C. OXY-combustion
D. pre-combustion capture
Answer: A
Supporting statement: There are three ways that this sequestration can be carried out: post-combustion capture, pre-combustion capture, and OXY-combustion.
Keywords: post-combustion capture, pre-combustion capture, OXY-combustion
Keyword Location: Para 3, Lines 1-2
Explanation: The text lists three specific capture methods: post-combustion, pre-combustion, and OXY-combustion. "Air-combustion" is not listed as one of these methods.
16. Which of the following practices helps accomplish biological sequestration?
A. reducing agricultural tillage
B. suppressing wildfires
C. restoring forests, wetlands and grasslands
D. all of the above
Answer: D
Supporting statement: Biological Sequestration is typically accomplished through conservation practices that enhance the storage of carbon (such as restoring forests, wetlands, and grasslands) or reduce CO2 emissions (such as reducing agricultural tillage and suppressing wildfires).
Keywords: restoring forests, wetlands, and grasslands
Keyword Location: Para 4, Lines 2-3
Explanation: The paragraph lists restoring forests, reducing agricultural tillage, and suppressing wildfires as practices that enhance or accomplish biological sequestration, meaning all three options are correct.
17. Which carbon sink is not used to sequester industrially produced CO2?
A. subsurface saline aquifers
B. plants and soil.
C. reservoirs and ocean water
D. aging oil fields
Answer: B
Supporting statement: Artificial processes have been devised to produce similar effects, including large-scale artificial capture and sequestration of industrially produced CO2 using subsurface saline aquifers, reservoirs, ocean water, aging oil fields, or other carbon sinks.
Keywords: subsurface saline aquifers, reservoirs, ocean water, aging oil fields
Keyword Location: Para 1, Line 6
Explanation: The text lists saline aquifers, reservoirs/ocean water, and aging oil fields as artificial or subsurface sinks for industrially produced CO2. Plants and soil are primarily associated with the natural or biological sequestration process described later in the passage.
Questions18-21
Do the following statements agree with the information given in the text above?
YES - if the statement agrees with the information
NO - if the statement contradicts the information
NOT GIVEN - if there is no information on this
18. Carbon sequestration slows the atmospheric and marine accumulation of greenhouse gases, which are released by burning fossil fuels.
Answer: NOT GIVEN
Explanation: While the text confirms sequestration mitigates global warming and targets CO2 from fuel-burning industries, it never mentions the effect on the marine accumulation of greenhouse gases. Therefore, this statement cannot be confirmed.
19. Natural biogeochemical cycling of carbon occurs between the atmosphere and reservoirs, such as by chemical weathering of rocks.
Answer: YES
Supporting statement: Natural biogeochemical cycling of carbon between the atmosphere and reservoirs, such as by chemical weathering of rocks.
Keywords: Natural biogeochemical cycling of carbon, atmosphere and reservoirs
Keyword Location: Para 2, Lines 7-8
Explanation: The text lists this exact description as one of the things "carbon sequestration may refer specifically to," confirming the statement.
20. Carbon sequestration leads to long-term storage of atmospheric carbon dioxide or other forms of carbon.
Answer: YES
Supporting statement: Carbon sequestration is the process involved in carbon capture and the long-term storage of atmospheric carbon dioxide or other forms of carbon to mitigate or defer global warming.
Keywords: Carbon sequestration, carbon dioxide
Keyword Location: Para 1, Lines 1-2
Explanation: The definition of carbon sequestration provided at the beginning of the text explicitly includes the long-term storage of atmospheric carbon dioxide or other forms of carbon.
21. The amount of carbon sequestered at a site does not depend on a balance between incorporation and release mechanisms.
Answer: NO
Supporting statement: However, the amount of carbon sequestered at a site depends on a balance between incorporation and release mechanisms.
Keywords: incorporation and release mechanisms
Keyword Location: Para 4, Line 9
Explanation: The text directly states that the amount of sequestered carbon depends on a balance between incorporation and release mechanisms. This contradicts the statement that it does not depend on this balance.
Read More IELTS Reading Related Samples
- Pterosaurs Reading Answers
- Study Centre Courses Reading Answers
- Self Study Tips Reading Answers
- Stanfield Theatre Reading Answers
- The Amazing Tuna Fish Reading Answers
- Your Guide to Entertainment in Westhaven Reading Answers
- Research on Improving Agricultural Yields in Africa Reading Answers
- Good Customer Service in Retail Reading Answers
- Its Almost Time for the Next Ripton Festival Reading Answers
- Helping Pupils to Choose Optional Subjects Reading Answers
- National Parks Reading Answers
- Use of Websites for Projects Reading Answers
- Discoveries on the basis of Deductive Reasoning Reading Answers
- Successions and Ecosystems Reading Answers
- How to prepare for a Presentation Reading Answers
- Professional Credentials Reading Answers
- An Early Cultural Tourist The Journey of Cyriacus of Ancona
- Train Travel Information Reading Answers
- The Importance of Business Cards Reading Answers
- The Young Persons Railcard Reading Answers
- Keele University Services for Students Reading Answers
- Introduction to the Grounds of Keele University Reading Answers
- A Young Italian Tradition Reading Answers
- Tuning up Your Leadership Skills Reading Answers
- Water Stress and Scarcity Reading Answers
- What are they Doing Up there Reading Answers
- Hard Languages Reading Answers
- What are they Doing Up there Reading Answers
- Registering as an Apprentice Reading Answers
- North Sydney Council Reading Answers
- A Brief History of Automata Reading Answers
- Working Time Regulation for Mobile Workers Reading Answers
- Marketing Advice for New Businesses Reading Answers
- Migrants and Refugees Racial Discrimination and Xenophobia Reading Answers
- Special Olympics Condition of Participation Reading Answers
- Social Smiling Reading Answer
- The History of Steel Reading Answer
- Why are we Ticklish Reading Answers
- Holiday Homes Online Ltd Technical Support Officer Reading Answers
- The Origin of Paper Reading Answers
- The Voynich Manuscript Reading Answers
- Creative Problem Solving Reading Answers
- Sorry Who Are You Reading Answers
- Miles Davis Icon and Iconoclast Reading Answers
- Global Response to Covid 19 Reading Answers
- Contact Lenses Reading Answers
- A buzz in the world of chemistry Reading Answers
- The Pick of This Summers Outdoor Music Festivals Reading Answers
- Newspapers Reading Answers
- Polo Reading Answers
Comments