Bees Reading Answers
Bees Reading Answers is an IELTS Reading Answer that contains 8 questions and needs to be completed within 10 minutes. Choose the correct letter, a, b, c, or d., and the diagram below shows the worker bee. Label the diagram and choose no more than two words from the passage for each answer.
The candidate's understanding and assessment of academic and general texts are examined in the IELTS Reading Section. Using IELTS Reading Practice Questions, you can increase your vocabulary, sharpen your critical reading skills, and become more familiar with the various question types in reading tasks. Furthermore, practice enhances vocabulary and improves analytical reading skills, both of which are necessary for success. It's critical to comprehend the guidelines for every question type and create effective ways to manage time to receive excellent band scores.
Check: Get 10 Free Sample Papers
Check: Register for IELTS Coaching - Join for Free Trial Class Now

Topic:
BEES
Worker bees are between 8-19 mm in length. They are divided into three distinct parts: head, thorax, and abdomen. They have an almost completely black head, a thorax that is golden brown and black with patches of orange, and yellow bands can be easily seen on the abdomen. At the front of the head are two antennae for sensing their environment. They have four single wings. The largest are called forewings, and the smallest hindwings. The hind legs are specialized for collecting pollen - each leg is flattened to form a pollen basket near the end of each leg.
Love them or hate them, we need bees to pollinate many important food crops, including most fruit and vegetables. Bee-pollinated crops are important sources of vitamins A and C, and minerals like calcium. By pollinating attractive wildflowers like bluebells and poppies, bees also help support the natural environment that people love — benefiting us culturally and economically, as well as ecologically. Calculations from the University of Reading show that €510 million of annual total crop sales in the UK are pollinated by bees and other insects.
What would happen if there were suddenly no more bees to pollinate these crops? This is a question being asked by farmers, beekeepers, and scientists because bees are now dying in their millions, and they want to know why.
It's widely recognised now that changes in agriculture are the main cause of bee decline across Europe. For example, hay meadows, which are full of many different plant species, have declined by 97 per cent since the 1930s, removing an important source of food for bees. This has happened because of the trend towards growing the same crop (monocultures) over large fields. This has reduced the diversity of flowers available and resulted in the removal of hedges. Species that have more specialised food needs, like the Shrill Carder Bee, have been particularly hard hit. It is now listed as an endangered species.
With less hedges, bees find it more difficult to move between feeding and nesting sites. This is because hedges act as corridors for bees to move along, but with less hedges, movement becomes more difficult. Pests and diseases are also a major threat to honey bees and other managed bees. The Varroa mite is thought to be one of the main causes of native honeybee loss. The impact on wild bees is harder to assess, but 'spill-over' of diseases and pests between wild and managed bees has increasingly been observed. Climate change has an effect as it can alter the timing of plant flowering or the time that bees come out of hibernation, which means bees may emerge before there is enough food available.
QUESTIONS 7 - 14
CHOOSE THE CORRECT LETTER, A, B, C, OR D.
7. Apart from pollinating crops, how else do bees help us?
A. economically
B. culturally
C. ecologically
D. all of the above
Answer: B
Supporting statement: bees also help support the natural environment that people love — benefiting us culturally and economically, as well as ecologically.
Keywords: benefiting, culturally and economically
Keyword Location: Para 2, Lines 3-5
Explanation: The text explicitly lists cultural, economic, and ecological benefits, meaning all are the benefits of bees
8. Why has the variety of flowers available for bees to pollinate fallen?
A. conservation measures
B. less hay meadows
C. fertilizers
D. urban development
Answer: A
Supporting statement: For example, hay meadows, which are full of many different plant species, have declined by 97 per cent since the 1930s, removing an important source of food for bees. This has happened because of the trend towards growing the same crop (monocultures)...
Keywords: hay meadows, declined, removing
Keyword Location: Para 3, Lines 2-3
Explanation: The decline in hay meadows and the trend toward monocultures (growing one crop) are the specific causes mentioned for the lack of flower diversity.
9. There are many reasons for the decline in bees, but what is one of the major reasons for the shrinking numbers of native honey bees?
A. Varroa mites
B. spill-over
C. managed bees
D. hard to assess
Answer: D
Supporting statement: The Varroa mite is thought to be one of the main causes of native honeybee loss.
Keywords: Varroa mite, honeybee loss
Keyword Location: Para 4, Line 4
Explanation: The text directly identifies the Varroa mite as the main cause of loss, specifically for native honeybees.
10. Why might bees end their hibernation at a different time?
A. to pollinate more flowers
B. to get more food
C. climate change
D. to emerge with other bees
Answer: C
Supporting statement: Climate change has an effect as it can alter the timing of plant flowering or the time that bees come out of hibernation
Keywords: Climate change, hibernation
Keyword Location: Para 4, Lines 6-7
Explanation: The text directly links the change in the timing of hibernation emergence to climate change.
QUESTIONS- 11 - 14
THE DIAGRAM BELOW SHOWS THE WORKER BEE. LABEL THE DIAGRAM.
CHOOSE NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS FROM THE PASSAGE FOR EACH ANSWER.
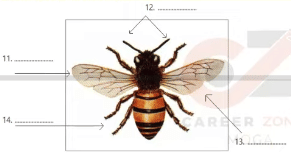
11………..
Answer: FOREWING / FOREWINGS
Supporting statement: The largest are called forewings, and the smallest hindwings.
Keywords: largest, forewings
Keyword Location: Para 1, Line 5
Explanation: The text specifies that the largest wings are the forewings.
12………..
Answer: ANTENNAE
Supporting statement: At the front of the head are two antennae for sensing their environment.
Keywords: head, two antennae
Keyword Location: Para 1, Line 4
Explanation: The text identifies the sensory organs on the head as antennae.
13………..
Answer: HINDWING / HINDWINGS
Supporting statement: The largest are called forewings, and the smallest hindwings.
Keywords: smallest hindwings
Keyword Location: Para 1, Line 5
Explanation: The text specifies that the smallest wings are the hindwings.
14…………
Answer: POLLEN BASKET
Supporting statement: The hind legs are specialized for collecting pollen - each leg is flattened to form a pollen basket near the end of each leg.
Keywords: leg, pollen
Keyword Location: Para 1, Lines 5-7
Explanation: The text describes the specialized part of the hind leg as the pollen basket.
Read More IELTS Reading Related Samples
- Professional Credentials Reading Answers
- An Early Cultural Tourist The Journey of Cyriacus of Ancona
- Train Travel Information Reading Answers
- The Importance of Business Cards Reading Answers
- The Young Persons Railcard Reading Answers
- Keele University Services for Students Reading Answers
- Introduction to the Grounds of Keele University Reading Answers
- A Young Italian Tradition Reading Answers
- Tuning up Your Leadership Skills Reading Answers
- Water Stress and Scarcity Reading Answers
- What are they Doing Up there Reading Answers
- Hard Languages Reading Answers
- What are they Doing Up there Reading Answers
- Registering as an Apprentice Reading Answers
- North Sydney Council Reading Answers
- A Brief History of Automata Reading Answers
- Working Time Regulation for Mobile Workers Reading Answers
- Marketing Advice for New Businesses Reading Answers
- Migrants and Refugees Racial Discrimination and Xenophobia Reading Answers
- Special Olympics Condition of Participation Reading Answers
- Social Smiling Reading Answer
- The History of Steel Reading Answer
- Why are we Ticklish Reading Answers
- Holiday Homes Online Ltd Technical Support Officer Reading Answers
- The Origin of Paper Reading Answers
- The Voynich Manuscript Reading Answers
- Creative Problem Solving Reading Answers
- Sorry Who Are You Reading Answers
- Miles Davis Icon and Iconoclast Reading Answers
- Global Response to Covid 19 Reading Answers
- Contact Lenses Reading Answers
- A buzz in the world of chemistry Reading Answers
- The Pick of This Summers Outdoor Music Festivals Reading Answers
- Newspapers Reading Answers
- Polo Reading Answers
- The Reindeer Reading Answers
- Drive on Low Beam in Fog Reading Answers
- Are You Being Bullied Reading Answers
- Theatre Reading Answers
- Can you Do Them at the Same Time Reading Answers
- Numeracy in Animals Reading Answers
- Non Pesticide Management of Crop in India Reading Answers
- Swordfish Reading Answers
- Mojito Reading Answers
- Calculating the Risk Reading Answers
- The Future of Getting Around in Cities Reading Answers
- Apollo 11 The First Moon Landing Reading Answers
- Potato Reading Answers
- Why Do Clocks go Clockwise Reading Answers
- Plastic Eating Worms Reading Answers
Comments