How Dangerous Waste Products are dealt with in Three countries IELTS Writing Task 1
IELTS Writing Task 1 is structured to test the candidate's ability to summarize and interpret visual data and information like charts, graphs, and tables. The task mainly involves identifying general trends, highlighting essential details from the bar charts, and making relevant comparisons with the available data. To obtain high marks on this writing task, candidates should have a great knowledge of English grammar and precise vocabulary with better comprehension skills.
Practicing various IELTS Writing practice papers allows candidates to interpret essential details and other information regarding the given topic like the pie charts below showing how dangerous waste products are dealt with in three countries. Regular practice of the writing paper enhances candidates' skills in identifying important details, and making relevant comparisons, leading to better clarity and overall performance in the IELTS Writing section.
Topic -
The pie charts below show how dangerous waste products are dealt with in three countries. Write a report for a university lecturer describing the information shown below. Summarize the information by selecting and reporting the main features and make comparisons where relevant. You should write at least 150 words.
Band 8 IELTS Answer
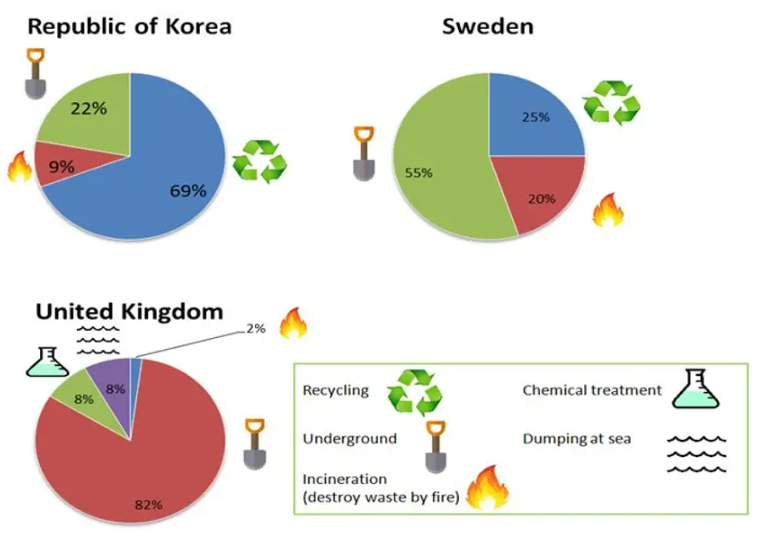
The pie charts shown in the above image clearly indicate how hazardous waste is perfectly managed and controlled in these three countries: the Republic of Korea, Sweden, and the United Kingdom.
In the Republic of Korea, most of the waste (around 69%) is disposed of by recycling waste, followed by underground disposal of the waste (around 22%), and a small fraction of the waste is disposed through the process of incineration, i.e., the waste is destroyed by burning it on fire, which is around 9% of the total waste.
Sweden, on the other hand, disposes of the highest portion of the total waste by underground disposal (around 55%). A significant portion of the total waste is recycled through several processes, which is around 25%, whereas 20% of the total waste is destroyed by burning the waste on fire, i.e., by the incineration process.
The United Kingdom disposes most of the waste through underground disposal, which is around 82% of the total waste management in the country. This is followed by dumping the waste in the sea (which is 8% of the total waste) and the same amount of waste (which is roughly 8% of the total waste) is managed through chemical treatment. The rest of the waste (which is 2% of the total waste) is destroyed by burning the waste in a fire, i.e., through the incineration process.
Band 7.5 IELTS Answer
The three pie charts shown in the above images are the methods of disposal of hazardous waste products in the Republic of Korea, Sweden, and the United Kingdom.
In the Republic of Korea, most of the hazardous waste (around 69%) is disposed of through the recycling process, whereas 22% of the total waste is managed by underground disposal of the waste and 9% of the total waste is managed by burning the waste on fire i.e., through incineration process.
In Sweden, the most conventional method of waste management is underground disposal of waste, responsible for 55% of the total waste which is followed by recycling the waste (around 25% of the total waste is managed by this process) and the remaining 20% of the total waste is managed by burning the waste on fire i.e., through incineration process.
The United Kingdom takes a different approach to waste management in their country, where a large proportion of dangerous waste is disposed of through underground disposal of the waste (around 82% of the total waste). On the other hand, 8% of the total waste is managed through Chemical Treatment, and the same amount of waste (around 8% of the total waste) is disposed of by dumping the waste at sea. Lastly, the remaining waste, which is around 2% of the total waste, is destroyed by burning it on fire through the incineration process.
Band 7 IELTS Answer
In the Republic of Korea, a substantial portion of hazardous waste is managed by recycling the waste (around 69% of the total waste), followed by underground disposal of the waste (around 22% of the total waste) with a small portion of the total waste (around 9%) is destroyed by burning it on fire through incineration process.
Sweden manages its waste management differently with 55% of the total waste disposed of through underground disposal of the waste, 25% of the total waste of the country recycled through different means, and the remaining 20% of the total waste destroyed by burning it on fire through the incineration process.
The United Kingdom relies primarily on underground disposal of waste through which 82% of the total waste of the country is managed through this process. Along with that, 8% of the total waste is managed by the Chemical Treatment process whereas the same amount of waste (which is around 8% of the total waste) is managed by dumping the waste at sea. Finally, the remaining 2% of the total waste is destroyed through the incineration process where the waste is destroyed by burning it on fire.
IELTS General Writing Task 1 Samples
- Most Common Advantages and Disadvantages of Bowen Island IELTS Writing Task 1
- Numbers of Visitors to the Ashdown Museum during the year before and the year after it was Refurbished IELTS Writing Task 1
- Main Reasons for Study Among Students of Different Age Groups IELTS Writing Task 1
- Three computer packages were downloaded from the internet IELTS Writing Task 1
- Pie Chart Showing Comparison of DifferentKindss of Energy Production in France IELTS Writing Task 1
- Line Graph Showing Paris Metro Station Passengers IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
- Nutritional Consistency Of Two Dinners IELTS Writing Task 1
- Participation of Boys and Girls in different Sports IELTS Writing task 1
- Line Graph Showing Percentage of Car Ownership in Great Britain IELTS Writing Task 1
- Cross-sections of Two Tunnels IELTS Writing Task 1
- Changes in Spending Habits of People in UK IELTS Writing Task 1
- Life Cycle of the Salmon IELTS Writing Task 1
- Visitor statistics for 1996,1998 and 2000 Table IELTS Writing Task 1
- The Percentage Of Water Used By Different Sectors Pie Chart IELTS Writing Task 1
- The Diagrams below Show the life cycle of the Silkworm and the Stages in the Production of Silk Cloth IELTS Writing Task 1
- Two Pie Charts showing the Percentages of Energy IELTS Writing Task 1
- The charts Below Show the Banana export in 1993 and 2003 IELTS Writing Task 1
- Number of visitors to three London Museums between 2007 and 2012 IELTS Writing task 1
- Comparison with Different Degrees Working in Engineering Company in 1980 and 2008 IELTS Writing Task 1
- Maximum Number of Asia Elephants between 1994 and 2007 IELTS Writing Task 1
- Average Maximum Temperatures for Auckland and Christchurch IELTS Writing Task 1
- Percentage of People Living Alone in 5 Different Age Groups in the US IELTS Writing Task 1
- Average Daily Minimum and Maximum of Two Air Pollutants IELTS Writing Task 1
- Journeys Made by Different Forms of Transport in Four Countries IELTS Writing Task 1
- Rates of Unemployment IELTS Writing Task 1
- Southland’s Main Exports in 2000 and Future Projections For 2025 IELTS Writing Task 1
- Different Sources of Air Pollutants IELTS Writing Task 1
- Write A Letter To Your Manager Asking Permission To Attend The Conference IELTS Writing Task 1
- Diagram Shows The Life Cycle Of Flowering Plants IELTS Writing Task 1
- Newly Graduated Students in the UK and their Proportions IELTS Writing Task 1
- Amount of Carbon Emissions in Different Countries During Three Different Years IELTS Writing Task 1
- Process Shows How Drinking Water Is Made Using Solar Power IELTS Writing Task 1
- The diagram shows the Process of the Water Treatment IELTS Writing Task 1
- Different Types of Crime in England and Wales From 1970 to 2005 IELTS Writing Task 1
- Population Figures For India And China IELTS Writing Task 1
- Use 6 Sentence Structures to Compare Numbers for IELTS Writing Task 1
- The Process of Pu-erh Raw Tea and Ripe Tea IELTS Writing Task 1
- Composition Of Household Rubbish In The United Kingdom In Two Different Years IELTS Writing Task 1
- Nitrogen Oxide Emissions By Four Vehicles IELTS Writing Task 1
- The Production of Coffee, Consumption, and Profits IELTS Writing Task 1
- Charts give Information about World Forest in Five Different Regions IELTS Writing Task 1
Comments