Changes in the Percentage of People taking Different Courses at a College in Canada IELTS Writing Task 1
IELTS Writing Task 1 evaluates important skills in creative writing, such as better English Grammar knowledge, precise vocabulary use, and comprehension skills.IELTS Writing Task 1 examines your capability to describe and summarize visual data like graphs, charts, maps, or tables the pie chart below showcases how many people in Canada are interested in taking different courses at a college.
Practicing different types of IELTS Writing Practice Papers improves your writing skills and allows the candidates to interpret the given information from the visual data. Just like the bar graph shown below showcases the percentage changes among the people of Canada taking different courses at a college. Daily practice of the IELTS Writing Papers enhances your writing skills and helps identify significant details from the visual data.
Topic: The pie charts below show the changes in the percentage of people taking different courses at a college in Canada.
Band 8 IELTS Answers
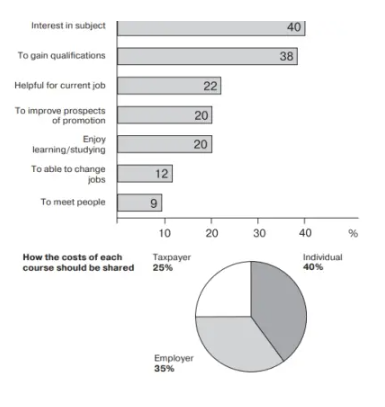
The bar chart shows the reasons why people enroll in a course at a Canadian College, whereas the pie chart indicates how the cost of each course should be allocated.
Among the given reasons for taking the courses, the most frequent reason is personal interest in a specific subject, mentioned by 40% of participants, followed by gaining qualifications (38%). Other reasons related to professional growth, like benefiting current jobs and improving promotion prospects, are mentioned by 22% and 20% respectively. Other important reasons include enjoying learning (20%), the ability to change jobs (12%), and socializing with other students (9%).
The pie chart indicates the preferred proportion of expenditure for these courses. Individuals are expected to contribute the most amount (which is around 40%), followed by Employers at 35% whereas the Taxpayers pay the remaining share, which is around 25%.
Band 7.5 IELTS Answers
The bar chart shows the main reasons individuals take courses at a Canadian college, whereas the pie chart shows the cost of these courses is equally shared among employers, individuals, and taxpayers.
According to the bar chart, the most prevalent reason for enrolling in a course is Personal Interest in a specific subject (40%). Right behind this, 38% of participants take a course to qualify for the desired course. Other important reasons include enhancing current job performance (22%), improving promotion prospects (20%), and enjoying studying (20%). Some other participants also intend to gain skills to change jobs (12%) or meet the other students of the college (9%).
The pie chart mainly indicates the preferred cost-distribution model for these courses. The majority (40% part) believe that Individuals should bear the largest part of the cost, followed by Employers (35%) whereas Taxpayers make the least contribution to the cost-distribution of the courses (which is around 25%).
Overall, Personal Interest and Career Growth are the primary reasons for taking courses, and there is an agreement in which individuals and employers should bear most of the financial expenses with taxpayers also playing an important role in bearing the cost for the courses provided at a college in Canada.
Band 7 IELTS Answers
The bar chart and pie chart shown in the above image offer essential information about motivation to enroll yourself at a Canadian college and the overall distribution of funds for several course costs.
The bar chart mainly highlights the main reasons why individuals are enrolled in a course. “Interest in the course” and “Gaining Qualifications” mainly dominate with 40% and 38% respectively. Other major motivations for improving job-related skills like “Helpful for Current Job” (around 22%), and “Improving Promotion Prospects” (20%). Other essential reasons like “Enjoying Learning (20%) are also equally significant just like other primary reasons. Reasons like “To be able to Change Jobs” and “To Meet People” are also significant reasons for enrolling in the courses at a Canadian college.
The pie chart mainly depicts the overall funding sources, with individuals bearing the largest contribution of the cost, around 40%. Employers primarily contribute around 35%, and taxpayers contribute the remaining share of 25%. Overall, the data shown in the visual data indicates that personal interests and career objectives mainly focus on course enrollment, while responsibility for funding is widely distributed across Employers, Taxpayers, and Individuals.
IELTS General Writing Task 1 Samples
- Life Cycle of the Salmon IELTS Writing Task 1
- Comparison with Different Degrees Working in Engineering Company in 1980 and 2008 IELTS Writing Task 1
- Maximum Number of Asia Elephants between 1994 and 2007 IELTS Writing Task 1
- Average Maximum Temperatures for Auckland and Christchurch IELTS Writing Task 1
- Percentage of People Living Alone in 5 Different Age Groups in the US IELTS Writing Task 1
- Average Daily Minimum and Maximum of Two Air Pollutants IELTS Writing Task 1
- Travelers in Different German Airports IELTS Writing Task 1
- Sales in Istanbul IELTS Writing Task 1
- Water used for different purposes in six areas IELTS writing task 1
- Household Cars IELTS Writing Task 1
- Population Aged 65 and Over of Three Countries IELTS Writing Task 1
- Internet Use in Six Categories by Age Group IELTS Writing Task 1
- Methods of Waste Disposal IELTS Writing Task 1
- Global Population Percentages and Distribution of Wealth IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
- Number Of Male And Female Students Studying Six Computer Science Subjects IELTS Writing Task 1
- Southland’s Main Exports in 2000 and Future Projections For 2025 IELTS Writing Task 1
- Different Sources of Air Pollutants IELTS Writing Task 1
- Different Types of Crime in England and Wales From 1970 to 2005 IELTS Writing Task 1
- The Graph below shows the Total Births and the Total Deaths in a European Country from 1950 to 2050 IELTS Writing Task 1
- Line Graph Showing Percentage of Car Ownership in Great Britain IELTS Writing Task 1
- Number of Books Read by Men and Women at Burnaby Public Library IELTS Writing Task 1
- Journeys Made by Different Forms of Transport in Four Countries IELTS Writing Task 1
- Population Aged 65 and Over of Three Countries IELTS Writing Task 1
- Automatic Photo Booth IELTS Writing Task 1
- Life Cycle of the Salmon IELTS Writing Task 1
- Water Usage in Australia IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
- Production of Potato Chips IELTS Writing Task 1
- A Table Showing Social and Economic Indicators for Four Countries in 1994 IELTS Writing Task 1
- Noise Pollution IELTS Writing Task 1
- Internet Use in Six Categories by Age Group IELTS Writing Task 1
- Number of houses built per year in two cities Derby and Nottingham IELTS writing task 1
- Percentage of Students Giving Good Ratings IELTS Writing Task 1
- Pie Charts giving Information about the Household Expenditure of an Average US Family IELTS Writing task 1
- The Production of Coffee, Consumption, and Profits IELTS Writing Task 1
- Charts give Information about World Forest in Five Different Regions IELTS Writing Task 1
- Online Shopping Sales for Retail Sectors in Canada IELTS Writing Task 1
- Write a Letter to Your Professor to Change the Presentation Date IELTS Writing Task 1
- Maps Showing Changes That Took Place in Youngsville in New Zealand IELTS Writing Task 1
- Pie Chart Showing Comparison of Different Kinds of Energy Production in France IELTS Writing Task 1
Comments