Percentage of Male and Female Students of Different Age Groups IELTS Writing Task 1
In IELTS Writing Task 1, candidates often need to explain data, like charts that show the percentage of male and female students in different age groups. To discuss both views clearly, it's important to use correct sentence structure, grammar, and good explanations. A strong introduction, body, and conclusion can help you get a higher score. Practicing with IELTS Writing practice papers is very helpful, as it prepares you for many different topics, like the charts showing the percentage of male and female students in various age groups
Topic:
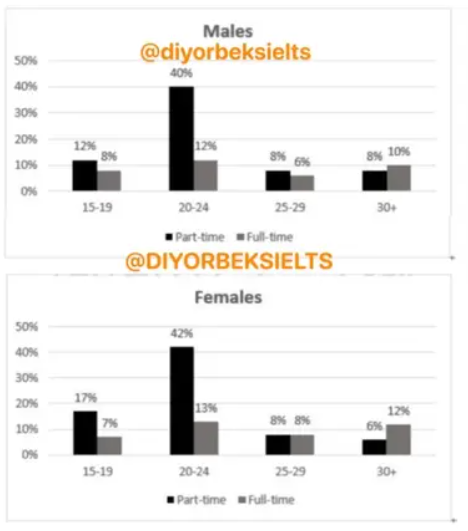
The charts below show the percentage of male and female students of different age groups who studied in Australia for full-time and part-time education in 2006.
Band 8 IELTS Answer
The bar chart compares data around the rate of boy and young lady understudies from distinctive classes who were given instruction in Australia for assorted sorts of time in 2006.
In general, it's clear that part-time examining for all sexual orientations who are 20-24 years old was higher than other categories of time to consider and ages, while understudies that are 25-29 were the most reduced in both females and guys at the time.
Typically in differentiating 15-19-year-old understudies in part-time instruction, females were more than guys, which spoke to 17% and 12%, individually. Understudies who are 20-24 had the most elevated extent of add up to examining and clearly part-time instruction for both sexual orientations was very indistinguishable at 14% for boys and 42% for young ladies.
Besides, the littlest extent of understudies was 25-29 a long time for ancient grown-ups, at that point the rate of both female and male understudies was comparable precisely, which accounted for 8%. By the way, part-time learning for female understudies who are over 30 was the least extent indeed than males meanwhile. The figures for them illustrated 6% for guys and 8% for male understudies in part-time instruction in 2006.
Band 7.5 IELTS Answer
The bar charts compare the rate of male and female understudies over distinctive age bunches in Australia who were enlisted in part-time and full-time instruction in 2006. In general, there's a noteworthy contrast between part-time and full-time instruction among the understudies aged 20-24 for both guys and females.
In detail, 12% of male understudies and 17 percent of female understudies enlisted in part-time instruction within the 15-19 age bracket, while understudies in full-time instruction were 8% and 7% for male and female understudies individually. The figure for part-time instruction for both sexes picked at 40% for guys and 42% for females. In the meantime, 12% of male and 13% of female understudies were in full-time instruction in this age group. The understudies matured 30 and over appeared at less rate for part-time instruction with 8% of guys and 6% of females, whereas male understudies and female understudies accounted for 10% and 12% in full-time instruction separately.
It's curious to note that the figure for both sorts of instruction appeared the same 8% for female understudies, yet a small distinction for male understudies, with 8% and 6% within the 25-29 age bracket.
Band 7 IELTS Answer
The bar charts compare the extent of male and female understudies concurring to two categories, to be specific full-time and part-time in Australia in 2006. In general, because it is clearly sufficient, the figures speaking to female understudies were somewhat more than that of guys, in common. Particularly, in both sexual orientation bunches the ones with the age of 20-24 rose as the foremost part-time understudies, whereas all other stats were tolerably comparative to each other with insignificant contrasts.
Beginning with the teenagers' bunch, 12% of the male understudies were examining part-time and 8% full-time, whereas the figures for females were 17% and 7% generally. Within the age group of 20-24, a whopping 40% of the male understudies were considering part-time instruction which is 2% less than that of female understudies, whereas 12% of the guys uncovered themselves in full-time instruction with 1% negative contrast as restricted to the females.
When it comes to the 25-29 age gathering, this was the gather in which the figures showed up to be very near. Nearly 8% of the understudies of both sexes took part-time and full-time instruction but for the male sound-related 2% less full-time understudies. In respect to the learners over 30, there was 2% more female in both part-time and full-time instruction, while generally 8% and 10% of the guys were attaining education
IELTS General Writing Task 1 Samples
- Write a Letter to Your Professor to Change the Presentation Date IELTS Writing Task 1
- Maps Showing Changes That Took Place in Youngsville in New Zealand IELTS Writing Task 1
- Pie Chart Showing Comparison of Different kinds of Energy Production in France IELTS Writing Task 1
- Line Graph Showing Paris Metro Station Passengers IELTS Academic Writing Task 1
- Nutritional Consistency Of Two Dinners IELTS Writing Task 1
- Participation of Boys and Girls in different Sports IELTS Writing task 1
- Line Graph Showing Percentage of Car Ownership in Great Britain IELTS Writing Task 1
- Cross-sections of Two Tunnels IELTS Writing Task 1
- Changes in Spending Habits of People in UK IELTS Writing Task 1
- Life Cycle of the Salmon IELTS Writing Task 1
- Visitor statistics for 1996,1998 and 2000 Table IELTS Writing Task 1
- The Percentage Of Water Used By Different Sectors Pie Chart IELTS Writing Task 1
- The Diagrams below Show the life cycle of the Silkworm and the Stages in the Production of Silk Cloth IELTS Writing Task 1
- Two Pie Charts showing the Percentages of Energy IELTS Writing Task 1
- A Charts Below Show the Banana export in 1993 and 2003 IELTS Writing Task 1
- Number of visitors to three London Museums between 2007 and 2012 IELTS Writing task 1
- Comparison with Different Degrees Working in Engineering Company in 1980 and 2008 IELTS Writing Task 1
- Maximum Number of Asia Elephants between 1994 and 2007 IELTS Writing Task 1
- Average Maximum Temperatures for Auckland and Christchurch IELTS Writing Task 1
- Percentage of People Living Alone in 5 Different Age Groups in the US IELTS Writing Task 1
- Average Daily Minimum and Maximum of two Air Pollutants IELTS Writing Task 1
- Journeys made by Different Forms of Transport in Four Countries IELTS Writing Task 1
- Rates of Unemployment IELTS Writing Task 1
- Southland’s Main Exports in 2000 and Future Projections For 2025 IELTS Writing Task 1
- Different Sources of Air Pollutants IELTS Writing Task 1
- Write A Letter To Your Manager Asking Permission To Attend The Conference IELTS Writing Task 1
- Diagram Shows The Life Cycle Of Flowering Plants IELTS Writing Task 1
- Newly Graduated Students in the UK and their Proportions IELTS Writing Task 1
- Amount of Carbon Emissions in Different Countries During Three Different Years IELTS Writing Task 1
- Process Shows How Drinking Water Is Made Using Solar Power IELTS Writing Task 1
- Diagram shows the Process of the Water Treatment IELTS Writing Task 1
- Different Types of Crime in England and Wales From 1970 to 2005 IELTS Writing Task 1
- Population Figures For India And China IELTS Writing Task 1
- Use 6 Sentence Structures to Compare Numbers for IELTS Writing Task 1
- The Process of Pu-erh Raw Tea and Ripe Tea IELTS Writing Task 1
- Composition Of Household Rubbish In The United Kingdom In Two Different Years IELTS Writing Task 1
- Nitrogen Oxide Emissions By Four Vehicles IELTS Writing Task 1
- The Production of Coffee, Consumption, and Profits IELTS Writing Task 1
- Charts give Information about World Forest in Five Different Regions IELTS Writing Task 1
- Online Shopping Sales for Retail Sectors in Canada IELTS Writing Task 1
Comments